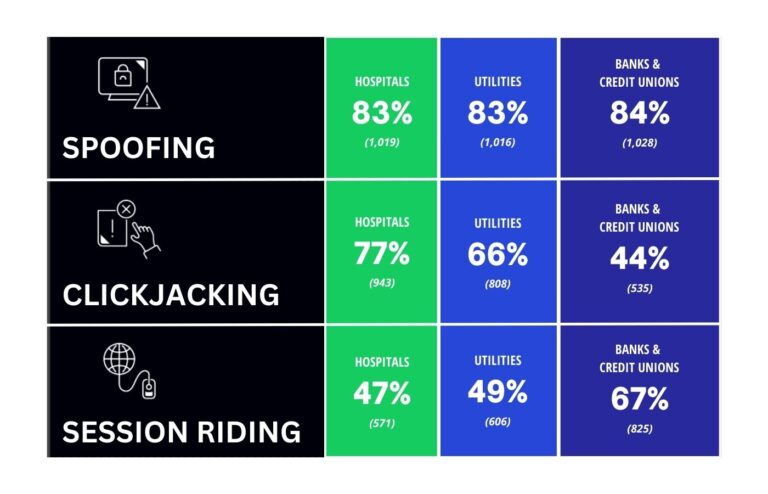
The cybersecurity news cycle often leads people to believe that only large enterprises with substantial budgets and expansive customer bases are the primary targets of attacks. However, this isn’t entirely true as small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) also hold sensitive information that is attractive to bad actors, and they are typically less prepared to safeguard it.
CyberCatch, based in Vancouver, has highlighted the state of security for SMBs in its recent Small and Medium-Sized Business Vulnerabilities Report (SMBVR), revealing that eight out of ten Canadian SMBs are at risk of a cyberattack. Many of these businesses operate in critical industry sectors such as finance and healthcare. The report’s findings all point to the need for strong cybersecurity measures in the SMB segment.