Threats, risks, and vulnerabilities are terms that are often used interchangeably in the context of cybersecurity. However, they are different concepts that require different approaches to mitigate them. Understanding the difference between them is crucial in developing an effective cybersecurity strategy.
PATHWAY COMMUNICATIONS
Know your threats before defeating them
Understanding the fundamentals of cyber attacks helps you develop an effective defence strategy.
The complex relationships between threats, risks, and vulnerabilities
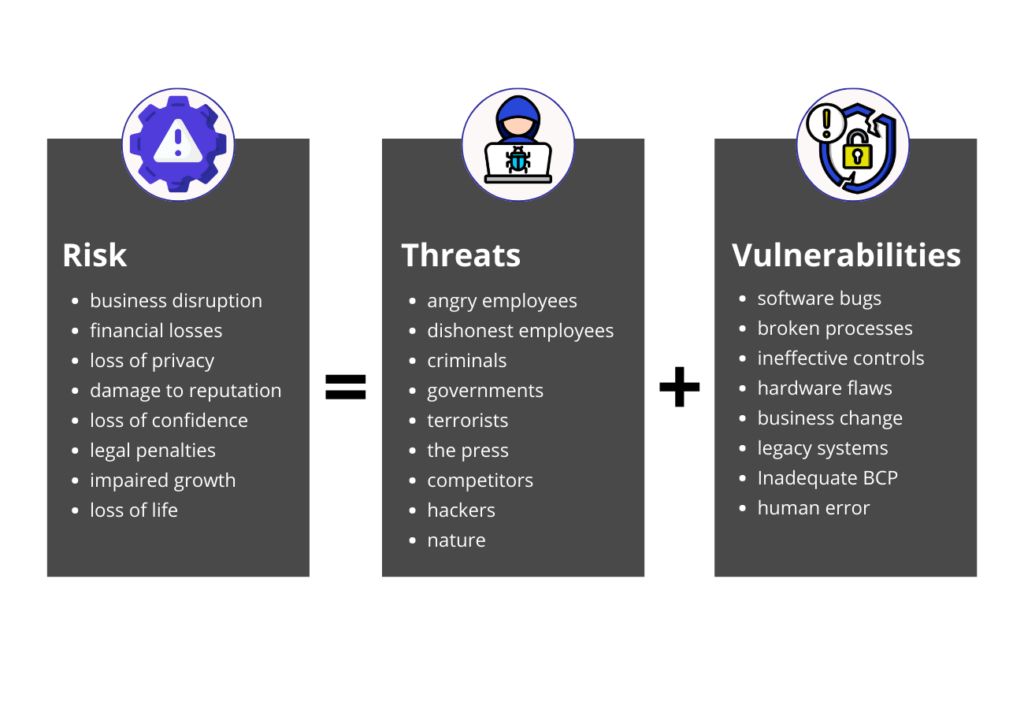
Threats
Cybersecurity threats are malicious activities that attempt to compromise or damage computer systems, networks, or devices. These threats can originate from a variety of sources, including criminal organizations, individual hackers, or even nation-states. Threats are constantly evolving, becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect with each passing day. But, implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems, can help protect against these threats.
To protect against cybersecurity threats, it is essential to understand the types of attacks that can occur and the methods that hackers use to gain unauthorized access. There are several types of threats that can pose a threat to cybersecurity, including but not limited to:
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to harm a computer system or network. It can include viruses, worms, and Trojan horses.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which cybercriminals trick individuals into providing sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or social security numbers.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
Denial-of-service Attacks
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack is when cybercriminals flood a network or website with traffic to overload it and make it unavailable to legitimate users.
Advanced Persistent Threats
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are long-term targeted attacks in which cybercriminals gain access to a network and remain undetected for an extended period of time.
Insider Threats
Insider threats are security risks that come from within an organization. They can include employees or contractors who intentionally or unintentionally compromise sensitive data or systems.
Zero-day Exploits
Zero-day exploits are vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the software vendor and can be exploited by cybercriminals before a patch is available.
Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in software, hardware, or IT systems that can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to data or systems. They are often caused by poor software design, coding errors, or misconfigured systems, and they can lead to security breaches and data loss. Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities is crucial to reducing the risk of a successful attack.
There are several types of vulnerabilities that can pose a threat to cybersecurity, including but not limited to:
Software Vulnerabilities
These are weaknesses in software programs or applications that can be exploited by attackers to gain access to sensitive data or systems.
Network Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities refer to flaws in a network’s architecture or configuration, which can allow attackers to bypass security controls and gain access to the network.
Human Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities refer to human behaviours, such as negligence, lack of awareness, or poor training, which can lead to security breaches.
Risks
Risk is the likelihood of a threat exploiting a vulnerability and causing harm to a system. In other words, a risk is the probability of something bad happening. Risks can be calculated based on the likelihood of a threat occurring and the impact it would have on a system. Understanding risks is critical to prioritizing cybersecurity efforts and allocating resources to mitigate them.
There are several types of risks that can pose a threat to cybersecurity, including but not limited to:
Human Error
This includes accidental or intentional actions taken by employees or insiders, such as clicking on a phishing email or sharing sensitive information with unauthorized parties
Social Engineering
This involves tricking people into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or log-in credentials, through tactics such as phishing, pretexting, or baiting.
Physical Security Risks
This includes risks related to the physical security of an organization’s facilities and equipment, such as theft, vandalism, or damage from natural disasters.
Third-party Risks
This includes risks posed by vendors, contractors, or other third parties that have access to an organization’s systems or data, but who may not have the same level of security controls in place as the organization itself.
Risk = Threats x Vulnerabilities

How to mitigate threats, risks, and vulnerabilities efficiently?
Mitigating threats, risks, and vulnerabilities requires a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity. So, having a reputed MSSP like Pathway as an ally in cybersecurity can help you achieve a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity, which includes continuous monitoring, threat detection, and rapid response to minimize the impact of cyber-attacks. Also, MSSPs offer a wide range of services, such as threat intelligence, risk assessments, vulnerability scans, penetration testing, incident response, etc., that come with industry-best expertise and advanced tools and technologies.

